- 如何为microcontroller制造二进制文件
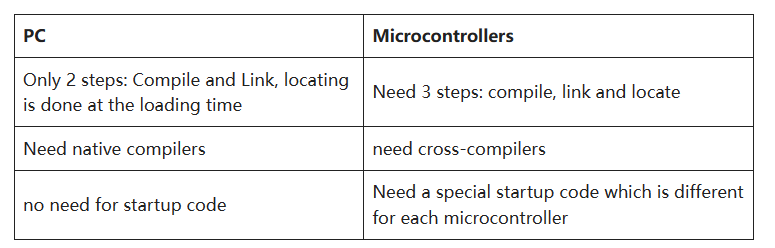
- Binary production for PCs vs microcontrollers
- Loading and Debugging
- GNU ARM Toolchain
- Tools to Produce The Binaries
- Tools to Help Debug Code
- 总结
- 参考
如何为microcontroller制造二进制文件
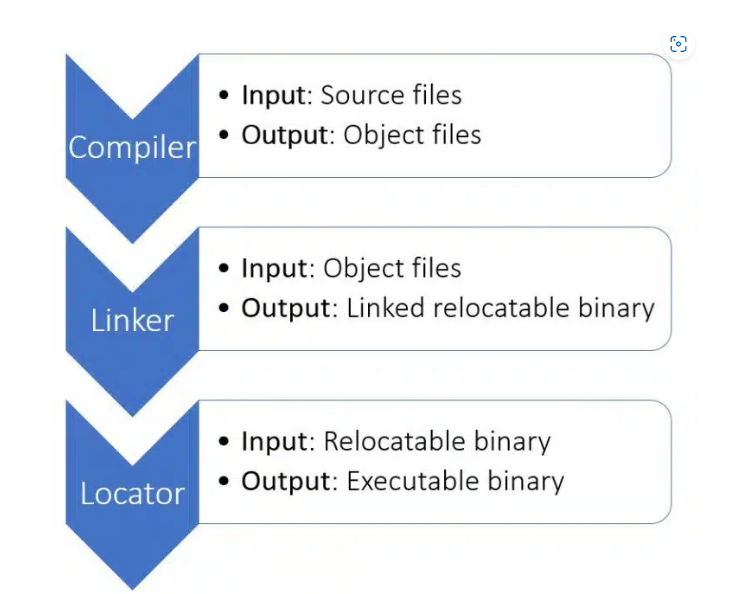
1. Compiler
将源代码(c/c++)转换成obj file,即将高级语言转换成机器可执行的低级语言
值得一提的是,因为我们是要在pc平台上生成嵌入式设备运行的程序,所以我们使用的是交叉编译器,交叉编译器与普通编译器的区别是,普通编译器用于在本地生成运行于本地平台的可执行代码,交叉编译器用于在本地生成目标平台的可执行代码
2. Linker
在第一阶段生成的obj文件中,通常分成三个部分,.text,.data,.bss
.text段存储代码部分
.data段存储已经初始化的全局变量
.bss段存储未初始化的全局变量
众所周知,高级代码语言允许我们将代码分成不同的模块,Linker的作用就是将各个模块的可执行文件合成一个最终的文件
方法也很简单,同样.text段的代码逢在一起,同样.data段的数据缝在一起,同样.bss段的数据缝在一起
3. Locator
因为不同类型的microcontroller都有不同的内存分布,来一个经典的:
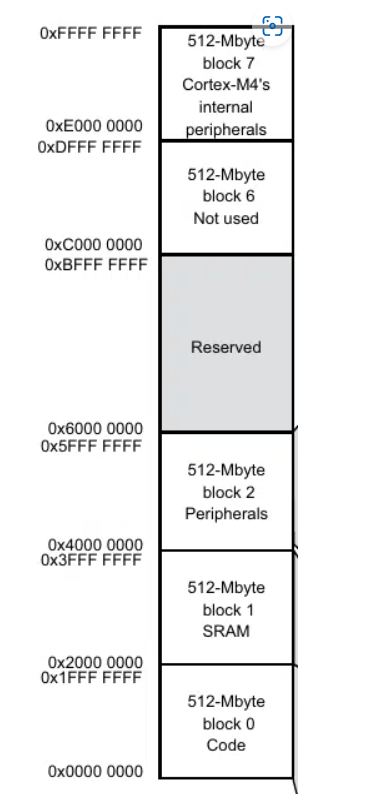
因此Locator的作用在于重新编排可执行文件的布局,使得该程序可以在microcontroller上运行,具体而言,Locator需要正确的标记.text段,.data段,.bss段的地址,以便.text段的内容加载到microcontroller的flash中,.data段、.bss段的内容刷到RAM中。
Startup Code
一个microcontroller的项目通常都有一个称作startup code的东西,通常该文件名称位startup.asm,startup.c,crt0.s,一但微控制器通电,它会从特定内存处加载复位向量(通常是0x00000000处,即startup code的代码起始地址),从通电到运行main函数之间,运行的都是start up code。The duty of the startup code is to take the machine from power-on point to the point where the main() function starts executing the application code.
在通电和运行main函数之间,startup code做了如下几件事情
1. initializes the important peripherals
2. the initialized global variables are copied over from the flash to the RAM. (we cannot do this while loading the code to the microcontroller because the RAM is volatile memory!)
3. The stack and heap are initialized on the free space of the RAM
4. main() is called
During the locating process this startup code must be placed at address 0x0000 and all the sections must be labeled with correct addresses so that the microcontroller can do the rest!
detailed STM32 memory layout
还是这张经典的图。

我们需要明确一点:因为stm32是32位arm程序,可以寻址的内存范围起始是4GB,然而实际上一个stm32微控制器是没有那么多内存空间的(一个100+的板子,要4gb的内存,你怕是想太多了😊)
现在我们要做的是仔细思考各个块之间到底放了些什么:
1. Code: 这该地址范围的前16字节包含复位向量表,其中包括初始堆栈指针和复位向量(复位向量指向startup code的代码起始位置),还有比较常用的是0x0800 0000开始的flash(或者rom)区间,startup code和 实际固件逻辑的代码都位于flash中。注意,此时data段和bss段在flash中也有备份,需要通过startup code拷贝到RAM中(因为flash和rom是只读的,需要拷贝到可读写的RAM中)
2. SRAM: 这个地址空间中,从低到高分布着 data段,bss段,heap段,stack段。注意:heap段向上增长,stack段向下增长,如果使用不慎,heap和stack是有可能重合的
3. Peripherals :这个范围内的地址主要用于访问和控制外设,如GPIO、串行通信接口、定时器等。采用MMIO的方式。通过将外设寄存器映射到这个区域,软件可以像访问内存单元一样访问这些寄存器,从而实现对外设的控制和配置。这种内存映射I/O方法简化了硬件和软件之间的接口,提高了处理器和外设之间的通信效率。注意,DMA控制器的相关配置也放在这里
4. internal peripherals: 其实这也是控制外设相关的部分,但是这个区间中主要包含与ARM Cortex-M内核相关的功能和寄存器,这些功能通常不是特定于STM32的,而是与ARM Cortex-M系列处理器共享的.
Binary production for PCs vs microcontrollers
Loading and Debugging
加载microcontroller程序到主板的flash上的过程叫做flashing.要想调试主板上的程序,我们需要一个主板上的特殊外设,名叫debug controller,用得到的比较著名的两个协议是是SWD和JTAG
但是SWD和JTAG协议相当于一门信号语言,PC端无法识别这种信号,所以为了能够让PC端识别这些协议,USB Debug adapters出现了,USB Debug adapters take data through USB signals and convert them into microcontroller readable JTAG/SWD signals.
Thus as we send this binary from the computer’s USB port via debug adapters, the microcontroller’s debug controller peripheral receives it and stores it onto the flash memory
在调试代码时,As we click these buttons, special instructions are sent to the debug controller which in turn controls the processor’s execution state.
GNU ARM Toolchain
arm-none-eabi
Tools to Produce The Binaries
 其中,1 主驱动程序,可以compile-link-locate一条龙
其中,1 主驱动程序,可以compile-link-locate一条龙
2是单纯的compile的部分,将汇编语言转换成obj
3是链接器
4是一个特殊的工具:
There are several formats an object file can be produced in. Popular formats include Extended Linker Format (.elf format) and Common Object File Format (.coff). But these formats are usually for running binaries on PCs and they contain some extra information about the binary.
For microcontrollers, the binaries are usually tightly packed without any extra metadata. objcopy is the tool responsible for taking the elf or coff binaries and pack them in a way that can be flashed onto the microcontroller!
elf axf coff的区别
AXF (ARM Executable Format):AXF 文件是专为 ARM 处理器设计的文件格式。它主要用于嵌入式系统和实时操作系统(RTOS)。AXF 文件格式基于 ELF,因此具有 ELF 文件的大部分特性。它支持在 ARM 架构上进行地址空间随机化(ASLR),并提供了一种描述程序执行的方式,包括代码段、数据段和符号表等。
ELF (Executable and Linkable Format):ELF 文件是一种通用的可执行文件、可链接文件和可重定位文件格式。它在许多不同的操作系统中被广泛使用,例如 Linux,FreeBSD,Solaris 等。ELF 文件包含了程序的二进制代码、数据、符号表和其他信息,以便在链接、加载和执行过程中使用。ELF 文件格式支持多种处理器架构(如 x86,x86-64,ARM,MIPS 等)和多种操作系统。
COFF (Common Object File Format):COFF 是一种较旧的可重定位文件格式,主要在微软的 Windows 系统和一些 Unix 系统(如 AIX)中使用。COFF 文件包含程序的二进制代码、数据、符号表等信息。与 ELF 相比,COFF 文件格式具有较低的可扩展性和灵活性。微软 Windows 系统已将其替换为更先进的 PE(Portable Executable)格式。
需要注意的是,直接烧录进嵌入式设备的通常是bin文件or hex文件
Tools to Help Debug Code

总结
- 用arm-none-eabi系列工具生成microcontroller可执行的程序
- 使用arm-none-eabi-gdb(debug server)进行调试
- OpenOCD会将可执行程序和gdb的调试命令 进行转换,发送给USB debug-adapter
- USB debug-adapter将USB信号转换为JTAG/SWD 信号或相反
- 开发板上的 debug-controler接收到信号后,进行相应的操作,并进行反馈
参考
https://embeddedinventor.com/a-complete-beginners-guide-to-the-gnu-arm-toolchain-part-1/