Unicorn
基于qemu的另一个开源项目。
现在变成了基础设施之一。像 angr,radare2都集成了Unicorn框架
Unicorn VS qemu
总得来说,unicorn专注于CPU的指令,不提供qemu那样对计算机其他设备的模拟。
优势还是有很多的:
- 框架:容易集成
- 灵活:即使没有上下文信息,即便没有文件格式(ELF),也能模拟运行,使用于dump出来的二进制片段
- 插桩: 提供qemu没有提供的动态插桩,能够自定义插桩技术
- 线程安全: qemu一般只能运行一个cpu,unicorn可以同时运行多个
- bindings: 说白了就是提供了各种语言的API接口,方便开发
- 轻量: 看大小就明白了,你安装qemu要装半天,unicorn很快就搞定了
- 安全: 因为模拟的方面少(就cpu),所以攻击面小(😀
UnicornAFL install
首先downloadAFL++,网址在https://github.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus
然后去unicorn_mode目录下运行./build_unicorn_support.sh
https://github.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus/tree/stable/unicorn_mode
Unicorn AFL运行原理
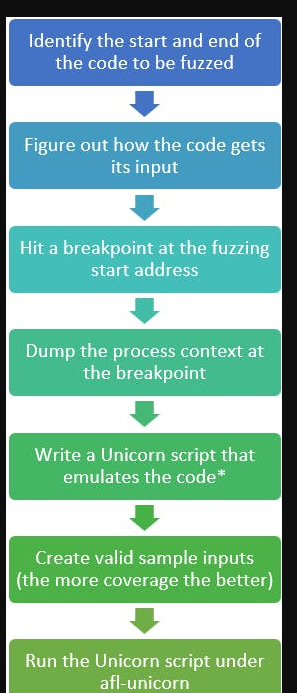 这张图节选自https://hackernoon.com/afl-unicorn-part-2-fuzzing-the-unfuzzable-bea8de3540a5
这张图节选自https://hackernoon.com/afl-unicorn-part-2-fuzzing-the-unfuzzable-bea8de3540a5
如图所示。
第一步你需要通过一些逆向操作,识别出你要fuzz的起始位置和终止位置,并找到代码是如何接受input的。
第二步说的是,需要尽可能的找到input的约束条件,因为在代码中,有的input可能直接被过滤掉了(无法到达你要测试的代码位置)
第三步,我们可以通过调试器运行到fuzz的起始地址,然后用Unicorn Context Dumper的脚本,保留这个情况下的程序状态
第四步,我们需要写一个harness,即unicornafl的运行脚本,加载程序的状态,接受afl的input,以及捕获crash的机制。
第五步,创造一些有效的input作为fuzz的seed,以便fuzz可以更有效的生成输入
第六步,跑脚本,期待捕获crash!
Unicorn API
有一些API需要了解
网址在这里https://github.com/kabeor/Unicorn-Engine-Documentation/
自行翻阅
实践
写了个程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
char * a = malloc(20);
printf("char addr:%p\n",a);
scanf("%s",a);
printf("%s\n",a);
}
编译程序后
写harness如下
import argparse
import os
import signal
import sys
from unicornafl import *
from unicorn.x86_const import *
DEBUG = 0
if DEBUG:
def log_to_file(message):
print(message)
else:
def log_to_file(message):
with open("harness_output.txt", "a") as f:
f.write(message + "\n")
pwd = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
BINARY_FILE = pwd+"/target"
# Memory map for the code to be tested
CODE_ADDRESS = 0x00000000 # Arbitrary address where code to test will be loaded
CODE_SIZE_MAX = 0x00010000 # Max size for the code (64kb)
STACK_ADDRESS = 0x00100000 # Address of the stack (arbitrarily chosen)
STACK_SIZE = 0x00010000 # Size of the stack (arbitrarily chosen)
DATA_ADDRESS = 0x00201000 # Address where mutated data will be placed
DATA_SIZE_MAX = 0x00010000 # Maximum allowable size of mutated data
# maintain allocator
heap_addr = DATA_ADDRESS
heap_size = 0
uc = Uc(UC_ARCH_X86,UC_MODE_64)
log_to_file("Loading file from {}".format(BINARY_FILE))
binary_file = open(BINARY_FILE,'rb')
binary_code = binary_file.read()
binary_file.close()
if len(binary_code)> CODE_SIZE_MAX:
log_to_file("file too large")
exit()
#code
log_to_file("mmap code")
uc.mem_map(CODE_ADDRESS,CODE_SIZE_MAX)
uc.mem_write(CODE_ADDRESS,binary_code)
#rip
start_address = CODE_ADDRESS+0x11A9
end_address = CODE_ADDRESS + 0x1205
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP,start_address)
#stack
uc.mem_map(STACK_ADDRESS,STACK_SIZE)
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RSP,STACK_ADDRESS+STACK_SIZE)
#data
uc.mem_map(DATA_ADDRESS,DATA_SIZE_MAX)
#hook
log_to_file("add hook func")
def hook_malloc(uc, address, size, user_data):
#log_to_file(">>> hook instruction at 0x%x, instruction size = 0x%x" % (address, size))
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RAX, heap_addr)
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP,address+size)
heap_size = uc.reg_read(UC_X86_REG_EDI)
#log_to_file("heap_size: {}".format(heap_size))
#log_to_file("set protect")
#uc.mem_protect(heap_addr,heap_size,UC_PROT_READ|UC_PROT_WRITE)
#uc.mem_protect(heap_addr+heap_size,0x1000,UC_PROT_NONE)
uc.hook_add(UC_HOOK_CODE,hook_malloc,begin=CODE_ADDRESS+0x11BA,end=CODE_ADDRESS+0x11BA)
def hook_scanf(uc, address, size, user_data):
#log_to_file(">>> hook scanf at 0x%x, instruction size = 0x%x" % (address, size))
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP,address+size)
array = uc.mem_read(heap_addr,heap_size)
#log_to_file("input content: {}".format(array))
uc.hook_add(UC_HOOK_CODE,hook_scanf,begin=CODE_ADDRESS+0x11EE,end=CODE_ADDRESS+0x11EE)
def hook_printf(uc, address, size, user_data):
#log_to_file(">>> hook printf at 0x%x, instruction size = 0x%x" % (address, size))
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP,address+size)
uc.hook_add(UC_HOOK_CODE,hook_printf,begin=CODE_ADDRESS+0x11D6,end=CODE_ADDRESS+0x11D6)
def hook_puts(uc, address, size, user_data):
#log_to_file(">>> hook puts at 0x%x, instruction size = 0x%x" % (address, size))
uc.reg_write(UC_X86_REG_RIP,address+size)
#log_to_file("start read heap")
data=uc.mem_read(heap_addr,30)
log_to_file("read_data:{}".format(data))
length = 0
for i in range(len(data)):
log_to_file("{}".format(data[i]))
if(data[i]!=0):
length+=1
continue
break
log_to_file("len data: {}".format(length))
if length>20:
os.abort()
uc.hook_add(UC_HOOK_CODE,hook_puts,begin=CODE_ADDRESS+0x11FA,end=CODE_ADDRESS+0x11FA)
# execute
log_to_file("start execute")
def place_input_callback(uc, input, persistent_round, data):
# Apply constraints to the mutated input
if len(input) > DATA_SIZE_MAX:
# log_to_file("Test input is too long (> {} bytes)")
return False
#log_to_file("input data: {}".format(input))
#log_to_file("input len: {}".format(len(input)))
uc.mem_write(DATA_ADDRESS, input)
uc_afl_fuzz(uc,BINARY_FILE,place_input_callback,[end_address])
#uc.afl_fuzz(BINARY_FILE, place_input_callback, [end_address])
# sudo afl-fuzz -U -m none -i ./sample_inputs -o ./output -- python3 harness.py @@
为unicorn AFL添加 heap allocator
众所周知,为许多 firmware 对于内存破坏的漏洞,并不能很好的发现和捕获。
为此,为了让fuzzer可以捕获到内存破坏漏洞,我计划写一个heap allocator,可以帮助fuzz firmware时,更有效的捕获漏洞。
from unicorn import *
from typing import Optional
import os
REDZONE_SIZE = 0 # double edge
DEBUG = 1
if DEBUG:
def heap_log_to_file(message):
return
#print(message)
else:
def heap_log_to_file(message):
with open("heap_message.txt", "a") as f:
f.write(message + "\n")
# help fuzz to get crash
def mem_trigger(uc, address, size, user_data):
heap_log_to_file("illegal read/write/execute in code_address 0x%x" % (address))
os.abort()
class HeapAllocator:
def __init__(self,uc:Optional[Uc],heap_start,heap_size):
heap_log_to_file("size:{}".format(heap_size))
self.uc = uc
self.heap_start = heap_start
self.heap_size = heap_size
self.heap_offset = heap_start
self.free_list = list()
self.free_size = list()
self.using_list = list()
self.using_size = list()
# initialize the uc memory status
self.uc.mem_map(self.heap_start,self.heap_size)
heap_log_to_file("heap mmap addr:{},size:{}".format(self.heap_start,self.heap_size))
# initialize the heap check mechanism
self.uc.hook_add(UC_HOOK_MEM_PROT,mem_trigger)
def malloc(self,size):
size += REDZONE_SIZE
#heap_log_to_file("malloc size:{}".format(size))
#1. get from free list
chunk = self.get_from_free_list(size)
if chunk is None:
#2. get from big heap
chunk = self.get_from_heap(size)
if chunk is None:
heap_log_to_file("error: memory is not enough,you need to mmap more size")
return None
return chunk
def free(self,addr):
heap_log_to_file("start free the addr:{}".format(hex(addr)))
if addr ==0:
heap_log_to_file("check the null pointer :{}".format(hex(addr)))
os.abort()
if addr in self.free_list:
heap_log_to_file("check the double free :{}".format(hex(addr)))
os.abort()
# delete from using list
size = self.delete_from_using_list(addr)
# check heap_overflow
input = self.uc.mem_read(addr+size,1)
if input[0]!=0:
heap_log_to_file("check hof")
os.abort()
# add chunk to free list
self.add_to_free_list(addr,size)
def get_from_free_list(self,size):
# just look for free_chunk_size>= size
for i in range(len(self.free_list)):
if(self.free_size[i]>=size):
chunk = self.free_list[i]
size = self.delete_from_free_list(chunk)
self.add_to_using_list(chunk,size)
return chunk
return None
def get_from_heap(self,size):
# just split the heap
if (self.heap_offset+size)<= (self.heap_start+self.heap_size):
chunk = self.heap_offset
heap_log_to_file("malloc chunk addr:{}".format(chunk))
self.add_to_using_list(chunk,size)
self.heap_offset += size
return chunk
else:
heap_log_to_file("heap space is not enough!")
return None
def add_to_free_list(self,addr,size):
heap_log_to_file("add to free list!")
self.free_list.append(addr)
self.free_size.append(size)
#self.lock_mem_protect(addr,size)
return
def delete_from_free_list(self,addr):
free_list_copy = self.free_list.copy()
free_size_copy = self.free_size.copy()
for i in range(len(self.free_list)):
if self.free_list[i] == addr:
del free_list_copy[i]
size = free_size_copy[i]
del free_size_copy[i]
break
self.free_list = free_list_copy
self.free_size = free_size_copy
return size
def add_to_using_list(self,addr,size):
self.using_list.append(addr)
heap_log_to_file("using list append:{}".format(addr))
self.using_size.append(size)
#self.unlock_mem_protect(addr,size)
return
def delete_from_using_list(self,addr):
heap_log_to_file("delete from using list!")
using_list_copy = self.using_list.copy()
using_size_copy = self.using_size.copy()
for i in range(len(self.using_list)):
if self.using_list[i] == addr:
del using_list_copy[i]
size = using_size_copy[i]
del using_size_copy[i]
break
self.using_list = using_list_copy
self.using_size = using_size_copy
return size
def unlock_mem_protect(self,addr,size):
#actually do nothing
true_chunk_addr = addr
true_chunk_size = size - REDZONE_SIZE
red_zone_back_addr = addr + size - REDZONE_SIZE
red_zone_back_size = REDZONE_SIZE
return
def lock_mem_protect(self,addr,size):
#actually do nothing
return
def ha_mem_check(self,addr,input):
# caclulate the input length
heap_log_to_file("heap_mem_write")
heap_log_to_file("input:{}".format(input))
length = 0
while input[length]!=0:
length += 1
heap_log_to_file("length:{}".format(length))
heap_log_to_file("address:{}".format(addr))
heap_log_to_file("using_lsit:{}".format(self.using_list))
heap_log_to_file("using_list len:{}".format(len(self.using_list)))
for i in range(len(self.using_list)):
chunk = self.using_list[i]
heap_log_to_file("chunk addr:{}".format(chunk))
chunk_size = self.using_size[i]
if (addr >= chunk) and ((addr+length) <= (chunk+chunk_size-REDZONE_SIZE)):
#self.uc.mem_write(addr,input)
heap_log_to_file("hit!")
return True
return False